
- Jun 18, 2024
- Professional Services
- Share
Understanding Logistics and Transportation: A Comprehensive Guide
Logistics and transportation are the lifeblood of modern economies, ensuring that goods move from manufacturers to consumers efficiently and reliably. While these terms are often used interchangeably, they represent different aspects of a complex and interdependent system. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of logistics and transportation, highlighting their significance, components, challenges, and future trends.
Introduction to Logistics and Transportation
Logistics encompasses the planning, implementation, and control of the flow and storage of goods, services, and related information from the point of origin to the point of consumption. It involves various functions, including inventory management, warehousing, order fulfillment, and distribution.
Transportation, on the other hand, is a subset of logistics focused specifically on the movement of goods and people from one location to another. It includes various modes such as road, rail, air, and sea transportation.
Importance of Logistics and Transportation
Economic Impact
Logistics and transportation are critical to economic growth and development. Efficient logistics systems reduce the cost of doing business, enhance competitiveness, and enable companies to reach global markets. They also create jobs and stimulate investment in infrastructure.
Supply Chain Efficiency
A well-organized logistics network ensures that products are delivered to the right place, at the right time, and in the right condition. This efficiency is vital for maintaining the flow of goods in industries like retail, manufacturing, and healthcare.
Customer Satisfaction
Timely and accurate delivery of goods boosts customer satisfaction and loyalty. In today's fast-paced world, consumers expect quick and reliable service, making logistics a key factor in customer experience.
Key Components of Logistics and Transportation
Transportation Modes
-
Road Transport: The most flexible mode of transportation, road transport is suitable for short to medium distances. It is commonly used for last-mile delivery and offers door-to-door service.
-
Rail Transport: Ideal for bulk goods over long distances, rail transport is cost-effective and environmentally friendly. It is often used for transporting commodities like coal, steel, and agricultural products.
-
Air Transport: The fastest mode of transportation, air transport is essential for high-value, time-sensitive goods. It is widely used in sectors like electronics, pharmaceuticals, and perishable items.
-
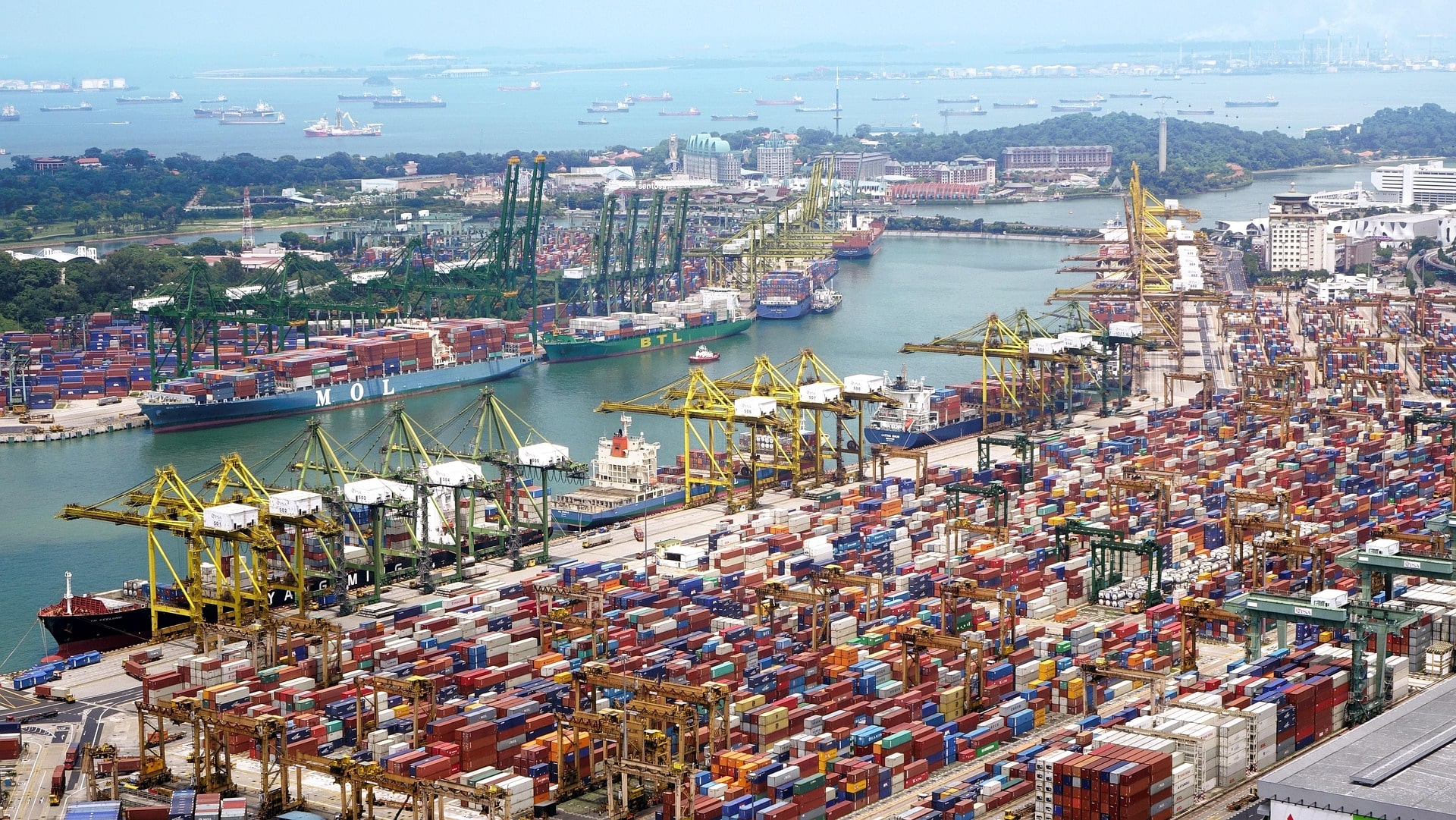
Sea Transport: Dominating international trade, sea transport is suitable for large volumes of goods over long distances. It is the most economical mode for bulk and oversized cargo.
-
Intermodal Transport: Combining multiple modes of transportation, intermodal transport leverages the strengths of each mode. For example, a shipment might travel by sea to a port, then by rail to an inland terminal, and finally by truck to its destination.
Warehousing
Warehousing involves the storage of goods until they are needed. It includes activities like receiving, storing, and dispatching products. Warehouses play a crucial role in managing inventory, balancing supply and demand, and ensuring the availability of products.
Inventory Management
Effective inventory management ensures that a company maintains optimal stock levels to meet customer demand without overstocking or understocking. Techniques like Just-In-Time (JIT) and Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) help streamline inventory processes.
Order Fulfillment
Order fulfillment encompasses the steps from receiving an order to delivering it to the customer. This process includes order processing, picking, packing, and shipping. Efficient order fulfillment is essential for customer satisfaction and retention.
Challenges in Logistics and Transportation
Rising Costs
Fuel prices, labor costs, and regulatory compliance contribute to the rising costs of logistics and transportation. Companies must find ways to manage these expenses without compromising service quality.
Infrastructure Limitations
Inadequate infrastructure, such as poor road conditions, congested ports, and outdated rail systems, can hinder the efficiency of logistics operations. Investment in infrastructure is crucial for improving transportation networks.
Environmental Impact
Transportation is a major contributor to greenhouse gas emissions and environmental pollution. There is increasing pressure on the industry to adopt sustainable practices and reduce its carbon footprint.
Technological Integration
The integration of advanced technologies, such as automation, artificial intelligence, and the Internet of Things (IoT), presents both opportunities and challenges. Companies must invest in technology to stay competitive while managing the complexities of implementation.
Supply Chain Disruptions
Natural disasters, political instability, and global pandemics can disrupt supply chains and create significant challenges for logistics and transportation. Companies need robust risk management strategies to mitigate these disruptions.
Future Trends in Logistics and Transportation
Digital Transformation
The adoption of digital technologies is transforming logistics and transportation. Innovations like blockchain, big data analytics, and cloud computing are enhancing transparency, efficiency, and decision-making.
Autonomous Vehicles
Autonomous trucks and drones are poised to revolutionize transportation by reducing labor costs, increasing safety, and improving delivery times. While still in the early stages, these technologies hold immense potential.
Sustainability Initiatives
Sustainability is becoming a core focus for the logistics industry. Companies are investing in green technologies, such as electric vehicles and renewable energy, to minimize their environmental impact.
Urban Logistics
With the growth of e-commerce, urban logistics is gaining prominence. Solutions like micro-fulfillment centers and smart delivery systems are being developed to address the challenges of last-mile delivery in densely populated areas.
Collaborative Logistics
Collaborative logistics involves sharing resources and information among companies to optimize supply chain operations. This approach can lead to cost savings, improved efficiency, and enhanced service levels.
Case Studies: Successful Logistics and Transportation Strategies
Amazon
Amazon's logistics network is a prime example of efficiency and innovation. The company's use of advanced technologies, such as robotics, AI, and data analytics, allows it to offer same-day and next-day delivery services. Amazon's extensive network of fulfillment centers and partnerships with various carriers ensure rapid order processing and delivery.
UPS
UPS is known for its global reach and commitment to sustainability. The company has invested heavily in alternative fuel vehicles and smart logistics solutions to reduce its carbon footprint. UPS also leverages advanced routing algorithms and real-time tracking to enhance delivery efficiency.
Maersk
As a leader in sea transport, Maersk has implemented digital solutions to streamline its operations. The company's blockchain-based platform, TradeLens, improves transparency and efficiency in the shipping industry by enabling real-time data sharing among stakeholders.
Conclusion
Logistics and transportation are fundamental to the functioning of modern economies. They ensure that goods are moved efficiently from producers to consumers, supporting economic growth and enhancing customer satisfaction. While the industry faces several challenges, advancements in technology and a focus on sustainability are paving the way for a more efficient and environmentally friendly future.
Understanding the components and complexities of logistics and transportation can help individuals and businesses appreciate the intricacies of getting products from point A to point B. As the industry continues to evolve, staying informed about the latest trends and innovations will be crucial for navigating the dynamic landscape of logistics and transportation.


Share